 |
 |
 |
| Missions
|
||
         |
The
Cassini mission The Cassini Orbiter’s mission consists of delivering a probe (called Huygens and provided by ESA) to Titan, and then remaining in orbit around Saturn for detailed studies of the planet and its rings and satellites. The principal objectives are to determine the three-dimensional structure and dynamic behaviour of the rings; to study the composition of the satellite surfaces and the geological history of each object; to determine the nature and origin of the dark material on Iapetus’ leading hemisphere; to measure the three-dimensional and dynamic behaviour of the magnetosphere; to determine the dynamic behaviour of Saturn’s atmosphere at cloud level; to study the variability of Titan’s clouds and hazes in time; and to characterise Titan’s surface on a regional scale. Twelve science instruments are carried by the orbiter, two of which, the Cassini Plasma Spectrometer (CAPS) and the Magnetometer (MAG), were developed by engineers of KFKI RMKI, including the current developers of SGF Kft., the Orbiter simulator (EGSE) was designed. The following instruments are also located on the orbiter: Cosmic Dust Analyzer (CDA); Composite Infrared Spectrometer (CIRS); Ion and Neutral Mass Spectrometer (INMS); Imaging Science Subsystem (ISS); Magnetometer (MAG); Magnetospheric Imaging Instrument (MIMI); Cassini Radar (RADAR); Radio and Plasma Wave Science (RPWS); Radio Science (RSS); Ultraviolet Imaging Spectrograph (UVIS); Visible and Infrared Mapping Spectrometer (VIMS); Cassini launched in October 1997 with the European Space Agency's Huygens probe. The probe was equipped with six instruments to study Titan, Saturn's largest moon. It landed on Titan's surface on Jan. 14, 2005, Cassini completed its initial four-year mission to explore the Saturn System in June 2008 and the first extended mission, called the Cassini Equinox Mission, in September 2010. Now, the healthy spacecraft is seeking to make exciting new discoveries in a second extended mission called the Cassini Solstice Mission, which goes through September 2017. In 2017, a probe was put into orbit very close to Saturn, and eventually burned up in its atmosphere. In this way, an unwanted potential contamination of Saturn's moon by microbes brought from Earth and surviving the 20-year space journey was ensured. It is no exaggeration to say that this successful mission is a milestone in the history of space exploration. CAPS includes an ion mass spectrometer (IMS) providing species-resolved measurements of the flux of positive atomic and molecular ions as a function of energy/charge vs. aperture entry direction; an ion beam spectrometer (IBS) that measures the flux of positive ions of all species as a function of energy/charge and entry direction; and also an electron spectrometer (ELS) to measure the flux of electrons as a function of energy/charge and entry direction. The Dual Technique Magnetometer (MAG) is a direct sensing Instrument that measures the strength and direction of the magnetic fields around Saturn. The magnetic fields are generated partly by the intensely hot molten core at Saturn’s center. Measuring the magnetic field is one of the ways to probe the core, even though it is far too hot and deep for an actual visit. Magnetometers are direct sensing instruments that detect and measure the strength of magnetic fields in the vicinity of the spacecraft. MAG consists of a vector/scalar helium magnetometer sensor, a flux-gate magnetometer sensor, a data processing unit, and three power supplies, plus operating software and electronics associated with the sensors. 08.October
2024
|
 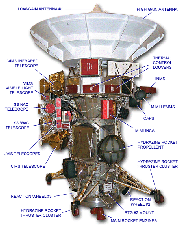 Scientific instruments on Cassini The CAPS istrument The MAG instrument Mil1553 IF boards |